Understanding electronic components is essential for anyone working in electronics. Among the most fundamental components are resistors, capacitors, inductors, semiconductors, and integrated circuits. Each plays a unique role in circuit design and functionality.
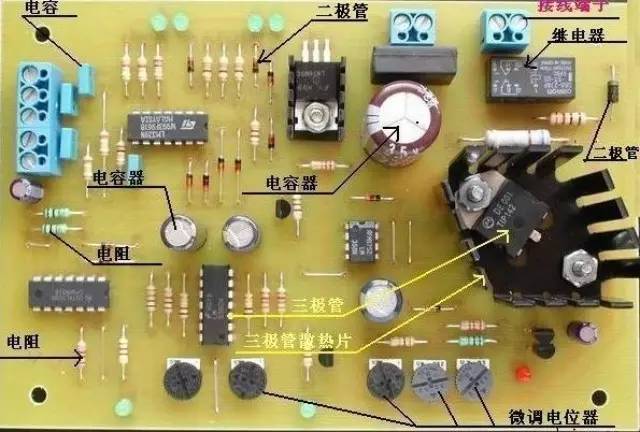
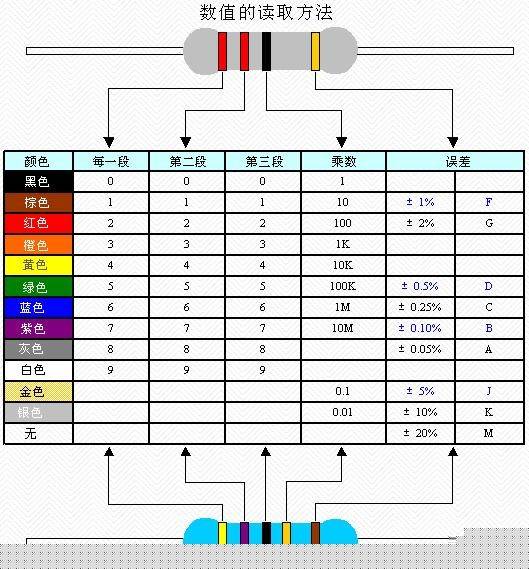
Resistors are used to limit current flow and divide voltages. Their resistance is measured in ohms (Ω), kilohms (kΩ), and megohms (MΩ). The naming of resistors typically includes four parts: the main name, material, classification, and serial number. Resistors can be categorized into wire-wound, thin-film, solid, and sensitive types such as varistors, thermistors, and photoresistors. They are marked using various methods like direct labeling, text symbols, digital codes, or color bands. For example, a four-band resistor has two significant digits, one multiplier, and one tolerance band, while a five-band resistor adds an extra digit for precision.
Chip resistors are often labeled with numbers that indicate their value. The third digit represents the power of ten. For instance, "100" means 10 ohms, "101" means 100 ohms, and so on. This method helps in quickly identifying the resistance without needing to refer to a chart or manual.
Capacitors store electrical energy and are used for filtering, coupling, and decoupling. Their capacitance is measured in farads (F), microfarads (μF), and picofarads (pF). Capacitors can be polarized (like electrolytic capacitors) or non-polarized. Polarized capacitors have a positive and negative terminal, and their polarity must be correctly observed during installation. Capacitance values are marked using direct labeling, text symbols, or color codes, similar to resistors but with different standards.
Inductors store energy in a magnetic field and are used in filters, transformers, and chokes. They are classified based on construction, core material, and application. Inductors work in conjunction with capacitors to form LC circuits, which are vital in radio and communication systems. Transformers, a type of inductor, are used to step up or step down voltages and isolate circuits from each other.
Semiconductor devices, such as diodes, transistors, and FETs, are the building blocks of modern electronics. Diodes allow current to flow in only one direction, while transistors act as switches or amplifiers. Field-effect transistors (FETs) control current flow using an electric field, making them ideal for high-frequency applications. These components are crucial in everything from simple LED circuits to complex microprocessors.
Integrated circuits (ICs) are miniature electronic circuits fabricated on a single piece of semiconductor material. They come in various forms, including analog, digital, and mixed-signal ICs. ICs are widely used in computers, smartphones, and other electronic devices due to their compact size, reliability, and efficiency. Proper handling and installation of ICs are essential to prevent damage from static electricity and overheating.
In summary, understanding the basics of electronic components is key to designing and troubleshooting circuits. Whether you're working with resistors, capacitors, inductors, semiconductors, or ICs, knowing their properties and how they interact will help you build more effective and reliable electronic systems.
ups inverter for home,10kw off grid invertergrid tie solar inverter,hybrid solar inverter,hybrid solar power inverter,solar power inverter for home
EMoreShare International Trade (Suzhou) Co., Ltd , https://www.emoreshare.com