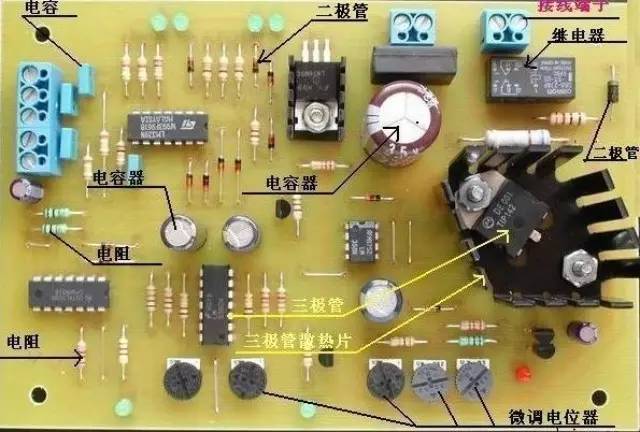
Knowledge of Electronic Components - Resistors
Resistance is the property of a conductor that opposes the flow of electric current. It is denoted by the symbol R and measured in ohms (Ω), kiloohms (kΩ), or megohms (MΩ). The model name of a resistor in China consists of four parts, excluding sensitive resistors: main name, material, classification, and serial number.
Resistors are classified into several types, including wire-wound resistors, thin-film resistors (carbon, synthetic carbon, metal, metal oxide, chemical deposition, glass glaze, and metal nitride films), solid resistors, and sensitive resistors (varistors, thermistors, photoresistors, force-sensitive resistors, gas-sensitive resistors, and humidity-sensitive resistors).
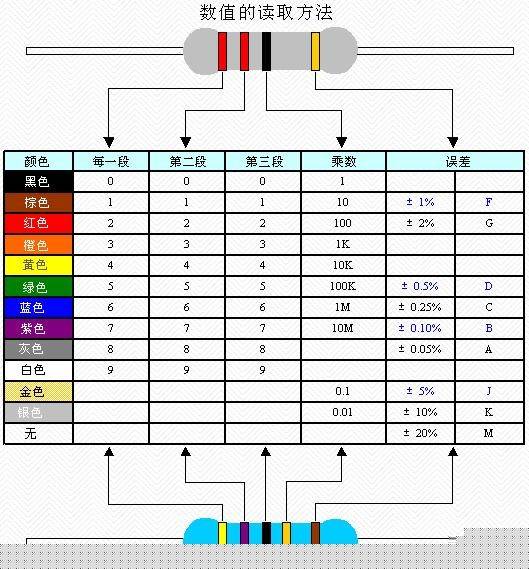
The resistance value on a resistor can be indicated using various methods. The straight standard method uses numbers and unit symbols directly. The text symbol method combines digits with letters to represent the nominal resistance, while the digital method uses three digits to indicate the resistance value. The color code method, commonly used in foreign resistors, marks the resistance and tolerance with colored bands. For example, black = 0, brown = 1, red = 2, etc., and gold/silver indicate ±5% or ±10% tolerance.
For chip resistors, the marking system varies. If the third digit is 0, it represents tens of ohms (e.g., 100 = 10 Ω, 990 = 99 Ω). A third digit of 1 indicates hundreds of ohms (e.g., 101 = 100 Ω, 151 = 150 Ω), and so on for higher values. The four-digit standard is also used, where the first three digits are significant, and the fourth is a multiplier (e.g., 1001 = 1 kΩ, 1002 = 10 kΩ, 1005 = 10 MΩ).
Understanding resistors is essential for any electronics project, as they are fundamental components in circuits for controlling current and voltage levels.
Knowledge of Electronic Components - Capacitors
Capacitance is the ability of a capacitor to store an electric charge. It is denoted by C and measured in farads (F), microfarads (μF), and picofarads (pF). Capacitors are widely used in electronic circuits for filtering, coupling, decoupling, and energy storage.
Capacitor models in China usually consist of four parts: name, material, category, and serial number. Electrolytic capacitors have polarity, which can be determined using a multimeter or by the length of the leads. The longer lead is typically the positive terminal, while the shorter one is negative.
Capacitors are categorized based on their polarity (polar or non-polar), structure (fixed, variable, trimmer), and dielectric type (organic, inorganic, electrolytic, air). Common types include aluminum electrolytic, tantalum, ceramic, film, and mica capacitors.
Capacitance values can be marked using direct labeling, text symbols, or color codes. For example, 01uF means 0.01 μF, while p10 represents 0.1 pF. Tolerance is often indicated by letter codes such as J (±5%), K (±10%), and M (±20%).
Capacitors play a crucial role in power supply filtering, signal coupling, and timing circuits. Understanding how to identify and use them is essential for any electronics enthusiast or professional.
Knowledge of Electronic Components - Inductors
Inductors are coils of wire wound around an insulating core, which can be air, ferrite, or iron-based. They store energy in a magnetic field and are used in filters, transformers, and oscillators. Inductance is measured in henrys (H), with millihenrys (mH) being more common in practical applications.
Inductors are classified based on their construction (single-layer, multi-layer, honeycomb), core material (air, ferrite, iron), and function (antenna, choke, transformer). They are often used in conjunction with capacitors to form LC circuits for tuning and filtering.
Transformers, a special type of inductor, transfer electrical energy between two circuits through electromagnetic induction. They are vital in power supplies and signal processing systems.
Relays are electromechanical switches that use inductors to control high-power circuits with low-current signals. They are widely used in automation and control systems.
Knowledge of Electronic Components - Semiconductor Devices
Semiconductors are materials with properties between conductors and insulators. Silicon and germanium are the most commonly used elements in semiconductor devices. They form the basis of diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits.
Diodes allow current to flow in one direction only. Zener diodes are used for voltage regulation, while LEDs emit light when forward-biased. The polarity of a diode can be identified using a multimeter or by the physical markings on the component.
Transistors are three-terminal devices that amplify or switch electronic signals. They come in NPN and PNP configurations and are used in amplifiers, switches, and logic circuits. Field-effect transistors (FETs), such as MOSFETs, are voltage-controlled devices and are commonly used in power electronics.
Integrated circuits (ICs) combine multiple components like transistors, resistors, and capacitors onto a single silicon chip. They are used in almost every modern electronic device, from simple calculators to complex computers.
Understanding the basics of semiconductors and their applications is essential for anyone interested in electronics, whether as a hobbyist or a professional engineer.
On grid solar system,Microgrid power system,outdoor energy storage cabinet,renewable energy storage system,Behind the meter battery storage
EMoreShare International Trade (Suzhou) Co., Ltd , https://www.emoreshare.com