The engine is an energy conversion mechanism, which is related to the power, economy and environmental protection of the car. It is the heart of the car, and the car can walk on it. The engine ignites the heat energy of gasoline or natural gas in a sealed cylinder, and pushes the piston to do work through the generated gas, which is converted into mechanical energy. This is the most basic working principle of the engine. All the structure of the engine is for energy conversion, and the engine has been with the car for more than 100 years. During this period, the design, manufacture, performance, control and other aspects of the engine have been greatly improved, but its basic principle is still the same. This article briefly introduces the basic components of the car engine and their respective functions.
This article refers to the address: http://
Engine designers continue to incorporate the latest technology into the engine, turning the engine into a complex mechatronic product. Now the engine's performance has reached near perfection, and automakers around the world regard engine performance as a competition. Highlights. In addition to paying attention to the embodiment of automobile power, the current car engine pays more attention to environmental protection-related aspects such as energy consumption and exhaust emissions, so that people can protect the environment and save resources while enjoying the car culture leisurely.
Basic composition of a car engine
Overall structure
Since the working principle of the engine is similar, the basic structure is similar. Gasoline engines are usually composed of five major systems: the diesel engine is usually composed of four major systems (no ignition system).
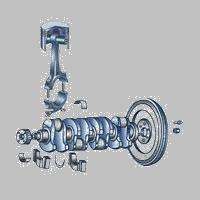
Engine assembly
Crank-link mechanism - the core to achieve thermal energy conversion, but also the basis for the assembly of the engine.
Gas distribution mechanism - to ensure that the cylinder is properly ventilated.
Fuel System - Controls the amount of fuel injected into the cylinder per cycle to regulate the engine's output power and speed.
Cooling system - controls the normal operating temperature of the engine.
Lubrication system - reduces friction and extends engine life.
Ignition system - timely supply of spark to gasoline engines (diesel engine without ignition system)
Starting system - rotates the crankshaft to complete the engine starting process.
Air Supply
The function of the valve train is to open and close the intake and exhaust valves in time according to the working sequence of the engine and the requirements of the working cycle of each cylinder, so that the combustible mixture (gasoline engine) or fresh air (diesel engine) enters the cylinder, and Exhaust gas is discharged into the atmosphere.
The four-stroke engine widely uses a valve cam type valve train, which is composed of a valve block and a valve train. According to different transmission modes, it can be divided into two types: timing gear transmission type and chain transmission type; according to the position of the cam shaft, it can be divided into lower parts, which can be divided into lower camshaft type and middle camshaft type. Upper camshaft type.
The lower camshaft type gas distribution mechanism is characterized in that: when the engine is in operation, the crankshaft drives the camshaft to rotate through a pair of intermeshing timing gears, and the valve opening degree is maximized when the convex edge of the cam rises to the highest position. When the convex tip of the cam moves downward, the valve and its transmission member return to the original position due to the elastic force of the valve spring, and the air passage is closed. Compared with the lower camshaft type gas distribution mechanism, the center and upper camshaft type gas distribution mechanism is mostly a timing chain or a timing belt transmission because the distance between the crankshaft and the camshaft is large. The center camshaft type eliminates the push rod; the upper camshaft type eliminates the tappet and the push rod.
Main parts
1. Valve group
The valve group generally consists of a valve, a valve seat, a valve guide, a valve oil seal, a valve spring and a valve lock piece.
(1) Valve valves are divided into two types: intake valve and exhaust valve. Their functions are to close the intake and exhaust channels respectively. The valve is composed of a head and a stem, and the head is tapered to fit the tapered surface of the valve seat. The cone angle of the head is generally 45°. The intake valve head diameter of the same engine is larger than the diameter of the exhaust valve head to increase the amount of inflation of the engine. The valve stem is cylindrical and cooperates with the inner bore of the valve guide. The end of the rod is provided with a ring groove for mounting the valve spring seat lock piece.
(2) Valve seat The valve seat is used to ensure the valve seal and transfer the heat from the valve head to the cylinder head. The valve seat is generally ring-shaped with a special alloy and is tightly mounted on the cylinder head.
(3) The valve guide valve guide is used to guide the valve to make a reciprocating linear motion to ensure that the valve and valve seat are closed properly. In order to prevent lubricating oil on the cylinder head from entering the combustion chamber from the gap between the valve and the valve guide, a valve oil seal is arranged at the upper end of the valve guide.
(4) Valve spring The valve spring is a cylindrical coil spring, which can quickly close the valve and press the valve head and the valve seat against each other to ensure the seal.
2, valve transmission group
The function of the valve transmission group is to open and close the valve in a timely manner according to the working sequence of the engine, and to ensure that the valve has sufficient opening.
(1) Camshaft camshaft is used to control valve opening and closing, and to drive parts such as gasoline pump, oil pump and distributor. The camshaft is provided with an intake cam, an exhaust cam, a journal, a gear for driving the oil pump and the distributor, an eccentric for pushing the rocker of the gasoline pump, etc. The intake and exhaust cams are important components of the camshaft, and they are important components of the camshaft. The order of arrangement on the camshaft is determined by the arrangement of the intake and exhaust passages.
(2) Timing gear and timing chain or timing pulley The drive of the crankshaft and camshaft is usually completed by timing gear, timing chain or timing transmission, such as CA6102, BJ492Q engine is timing gear transmission Beijing Cherokee car engine is a timing chain drive; Shanghai Santana car engine is a timing belt drive.
The four-stroke engine crankshaft rotates for two weeks, the camshaft should rotate for one week, so that the intake and exhaust valves are opened and closed once, and the valve opening and closing timing must be compatible with the needs of each cylinder working cycle. Therefore, whether it is a gear transmission or a chain drive, it must be assembled according to the specified mark, and its mark is generally a pit of the tooth portion.
(3) The function of the valve lifter tappet is to transmit the thrust of the cam to the push rod or the valve. The type of tappet is mushroom type, cylindrical non-hydraulic type, cylindrical hydraulic type, cylinder type hydraulic type, etc. The cylindrical hydraulic type tappet has no valve clearance, which can reduce the noise of the engine, but the precision is strict and the cost is high. Mostly used in high-class car engines.
(4) The function of the valve push rod is to transmit the thrust of the tappet to the rocker arm to drive the valve to open. The upper and lower ends of the push rod are heat treated and polished to improve wear resistance; the shaft has both solid and hollow.
(5) The rocker arm and rocker arm shaft assembly is used to change the thrust direction of the push rod (lower camshaft type), tappet (center camshaft type) or cam (upper camshaft type) to open the valve . The rocker arm shaft assembly is fixed on the upper part of the cylinder head, mainly by a rocker arm and a rocker arm.
The shaft support is composed of the rocker arm and the two arms are not equal in length, so that the tappet and the push rod can obtain a larger opening of the valve with a smaller lift. One end of the long arm of the rocker arm corresponds to the valve stem, and one end of the short arm is provided with an adjusting screw and a nut for adjusting the clearance of the valve foot. The rocker arm shaft is a hollow shaft, and a lubricating oil passage is penetrated with the rocker arm shaft support and the rocker arm to lubricate the friction surface of the gas distribution mechanism portion.
Crank Mechanism
The crank two-bar mechanism converts the gas pressure generated after the fuel is burned into the torque of the crankshaft rotation through the piston and the connecting rod during the power stroke; then, the intake, compression, and exhaust three auxiliary strokes are completed by the inertia of the flywheel. The crank-link mechanism cylinder crankcase group, the piston connecting rod group and the crankshaft flywheel group are composed of three parts.
1, cylinder block and crankcase
The cylinder block and the crankcase are usually cast together, collectively referred to as the cylinder block. It is the outer casing and assembly base of the engine. It is generally made of high-quality alloy cast iron or aluminum alloy. The structure is in the form of in-line type, V-type and opposite type. The cylinder block of an inline six-cylinder engine. The engine is an inline six-cylinder water-cooled gasoline engine. The cylindrical space inside the cylinder is called a cylinder, and the cylinder surface is called a cylinder wall.
The cylinder is the place where the gas is exchanged and burned, and it is also the track of the piston movement. In order to ensure the sealing of the piston and the cylinder and reduce the wear, the cylinder wall should have an effective high machining accuracy and a low surface roughness. In order to dissipate the heat of the cylinder during operation, a sandwich cavity capable of accommodating the coolant is formed between the cylinder block and the cylinder liner body, which is called a water jacket.
There are 7 main bearing seats in the lower part of the cylinder block for mounting the crankshaft flywheel set. The side of the cylinder block is provided with a tappet chamber for mounting the valve transmission mechanism. The cylinder head is mounted on the upper surface of the cylinder block, the oil pan is mounted on the lower plane, and the timing gear cover is mounted on the front end surface, and both are padded and sealed with bolts. The flywheel housing is mounted on the rear end surface of the cylinder block.
In order to enhance the wear resistance of the cylinder block and prolong the service life of the cylinder block, the cylinder block is mostly provided with a cylinder liner. The cylinder liner is divided into dry and wet. The dry cylinder liner is not in contact with the coolant. To prevent the cylinder liner from swaying downward, it can be restrained at the upper (lower) stop. The outer surface of the wet cylinder liner is directly in contact with the coolant. To prevent leakage of coolant, 1 to 3 rubber seals are installed at the lower end of the cylinder liner.
2, oil plate
The function of the oil pan is to store the lubricating oil, so it is commonly called the oil pan. It is generally stamped from thin-walled steel with a stabilizing oil baffle inside to prevent excessive lubrication, and a drain plug at the bottom for oil change.
3, cylinder head gasket
The cylinder head gasket, commonly known as the cylinder bed, is installed between the cylinder head and the cylinder block. Its function is to seal the joint plane between the cylinder block and the cylinder head to prevent air leakage, leakage of coolant and oil leakage. The cylinder head gaskets are mostly made of asbestos sheet material, some are made of asbestos board and two breads of copper or iron, and some are made of two layers of intermediate steel sheets suitable for the suitable latex asbestos board. The combustion chamber holes are double-layered or single-layered metal to prevent the combustion gas from damaging the asbestos layer.
4, cylinder head
The main function of the cylinder head is to close the upper part of the cylinder and form a combustion chamber with the top of the piston. The cylinder head has a combustion chamber, a water jacket, a spark plug seat hole (the diesel engine has a fuel injector mounting hole), an intake and exhaust passage, a valve seat, and a valve guide seat hole. The upper part is provided with a rocker arm shaft assembly, which is closed by a cylinder head cover, and a sealing point pad is arranged between the joint surfaces.
Gasoline engine cylinder heads are generally integral, but there are exceptions. For example, the EQ6100-1 engine is two cylinder heads. A diesel engine with a large cylinder diameter adopts one cylinder, one lid or two cylinders and one lid, and no more than three cylinders and one lid to prevent deformation of the cylinder head.
Ignition system
Composition: The traditional type consists of a battery, a generator, an ignition coil, a breaker, a spark plug, and the like. The conventional and conventional ignition systems are similar, except that the electrical components are used instead of the breakers. The electronic ignition type is all-electronic ignition system, completely eliminating the mechanical device, and the electronic system controls the ignition timing, including battery, generator, ignition coil, spark plug and electronic control system.
Function: In the gasoline engine, the combustible mixture in the cylinder is ignited by electric spark. For this purpose, a spark plug is installed on the cylinder head of the gasoline engine, and the head of the spark plug protrudes into the combustion chamber. All devices that are capable of generating sparks between the spark plug electrodes on time are called ignition systems.
Fuel supply system
effect
The function of the gasoline engine fuel system is to formulate the pure air and gasoline into a proper proportion of combustible mixture according to the needs of different working conditions of the engine, and the exhaust gas generated after being sent into each cylinder for combustion is discharged into the atmosphere.
basic component
The basic composition of the carburetor fuel system, which can be divided into gasoline supply devices (including gasoline tanks, gasoline filters, gasoline pumps), air supply devices (including air filters, intake muffler, cold and warm air conversion mechanisms, etc.) ), a mixture forming device (carburetor), an intake and exhaust device (including an intake branch pipe, an exhaust branch pipe, and a muffler).
cooling system
Composition: Water-cooled type consists of water jacket, water pump, radiator, fan, thermostat and so on. The air-cooled type consists of a fan and a heat sink.
Function: The function of the cooling system is to dissipate part of the heat absorbed by the heated parts in time to ensure that the engine works at the optimum temperature.
Lubrication system
Composition: It consists of oil pump, filter, pressure limiting valve, oil passage, oil filter and so on.
Function: The function of the lubrication system is to deliver a quantitative cleaning lubricant to the surface of the relatively moving parts to achieve liquid friction, reduce frictional resistance and reduce wear and tear on the parts. The surface of the part is cleaned and cooled.
Starting system
Composition: It consists of a starter and its accessories.
Function: In order to make the engine transition from the static state to the working state, the crankshaft of the engine must first be rotated by external force to make the piston reciprocate. The combustible mixture in the cylinder burns and expands work, pushing the piston downward to make the crankshaft rotate. The engine can run on its own and the work cycle can be automated. Therefore, the crankshaft starts to rotate under the action of an external force until the engine starts to automatically idle, which is called starting of the engine. The device required to complete the starting process is called the starting system of the engine.
What are the basic components of a car engine? The above is a brief introduction to Xiaobian. I believe that readers and friends have a deeper understanding of the car engine. Automotive engines also require regular maintenance, such as the use of appropriate quality grades of lubricants, regular oil changes and filter elements, good crankcase ventilation, regular crankcase cleaning, etc., to increase engine life.
Ceramic Heater is ued in controllable aural various heat treatment furnace,to avoid the contact of elding burning outcome or to avoid the corrosion of furnace gas to heating element.The process(the conversion of elding burning or electric energy) is put into refractory steel tube and let amount of heat radiate by wall of tube.This device is called as heater tube.
Twist and turn resistance wire in axial direction,that is,the single resistance wire is bended to U shape,then in series or parallel connection mutually.This kind of electrothermal heater tube is called bending resistance wire heater tube.This tube,because fall of screening of resistance wire,in intratubal upper surface load,can insure prolong life span.
Ceramic heating element is a heating element and the ceramic through high temperature sintering, fixed together made of a heating element, according to the body temperature level to adjust the size of the resistance, which can be constant temperature in the set value, not overheating, with Energy saving, safety, long life and other characteristics. This heater does not light at work, no open flame, no oxygen consumption, soft air supply, with automatic temperature function. PTC ceramic heater output power in the 800-1250 watts, you can freely adjust the temperature, no light consumption when working, with automatic switching devices, energy efficient, energy safe. PTC ceramic heater uses most of the bathroom in the bathroom heater and some small bedroom heating. The rainy season takes into account the relatively dry indoor air in the northern part of the winter, the part of the heating in the bedroom PTC ceramic heater and humidifier function together, the introduction of humidification heater, warm hot air with the humid air blowing together , People feel very comfortable, and almost no noise. As consumers continue to improve the demand on the market derived from the novel products - fireplace - to simulate the flame, ceramic heating, resulting in warm air, creating a warm European and American style (power up to 1800W). The new appearance of a PTC ceramic heater appearance and ordinary oil-like heater like, but the use of enamel heat sink. Features a heat sink, thin shape, a protective cover, the use of security. Some of the more advanced products used in the room with infrared remote control, regular shutdown, fall automatically power and heating and other functions, can be regarded as fully functional.
Ceramic Heater
Ceramic Heaters, Small Ceramic Heater, Portable Ceramic Heater, Electric Ceramic Heater, Ceramic Room Heater
Ningbo APG Machine(appliance)Co.,Ltd , http://www.apgelectrical.com