The LIN bus is a cost-effective serial communication network designed for automotive distributed electronic systems. It serves as a complement to more complex networks like the Controller Area Network (CAN), making it ideal for applications that do not require high bandwidth or advanced fault tolerance. Based on the SCI (UART) data format, the LIN bus operates in a single master/multi-slave configuration, which makes it a simplified variant of UART communication.
**LIN Bus Working Principle**
LIN nodes are typically located close together, and the system uses a single wire for data transmission, with a maximum length of up to 40 meters. The master node is connected to a 1kΩ resistor linked to the 12V power supply, while each slave node has a 30kΩ resistor connected to the same voltage source. This setup allows each node to pull down the bus voltage through its internal transmitter, ensuring stable communication.
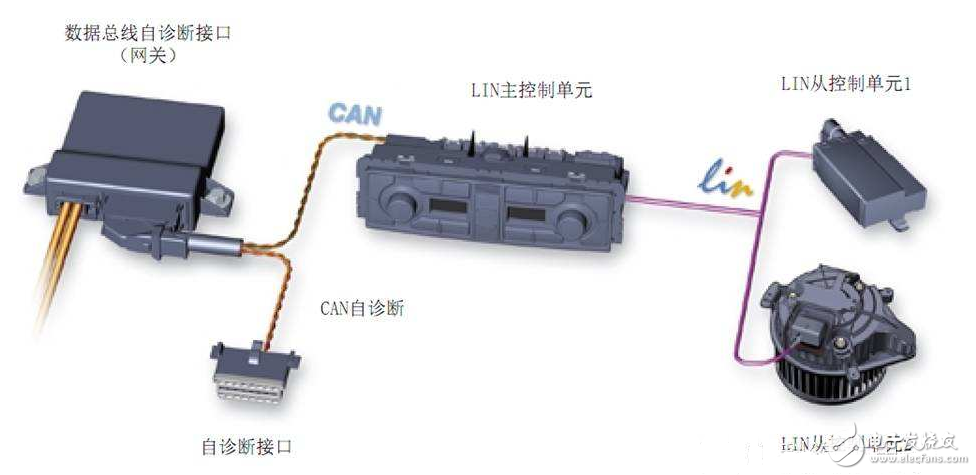
**Main Control Unit**
The LIN master control unit connects to the CAN data bus, monitoring data flow and speed. It sends message headers, determines when and how data is transmitted, and acts as a bridge between the LIN and CAN buses. It also enables self-diagnosis for both itself and connected LIN slave units.
**Information Structure of the Main Control Unit**
The main control unit initiates each data transfer by sending a message header over the LIN bus. This header includes a synchronization phase and an identifier byte, followed by 2, 4, or 8 bytes of data. The identifier helps determine whether the data should be sent to a specific slave unit. The data segment contains the actual information, while a checksum at the end ensures data integrity. The master unit cycles through all connected devices in a round-robin fashion.

**LIN Slave Control Unit**
In a LIN network, the slave control units rely entirely on the master unit for communication. They can only transmit data when commanded by the master. These units may include sensors, actuators, or other single-function devices. Sensors act as input devices, converting physical measurements into digital signals for transmission via the LIN bus. Some components use a single wire for communication, simplifying the wiring harness.
LIN actuators are intelligent components that receive commands from the master unit. The master monitors the actuator’s status using built-in sensors, compares it with the desired state, and issues appropriate instructions. Once a command is issued, the sensor and actuator respond accordingly. The slave unit waits for instructions and communicates only when necessary. If it needs to exit sleep mode, it can send a wake-up signal independently. The LIN master unit is installed within the vehicle's LIN bus system, serving as the central controller for all connected devices.
I-type Inductance Core,I Inductor Model,Ring I-type Inductance,Design Of I-Shaped Inductor
Xuzhou Jiuli Electronics Co., Ltd , https://www.xzjiulielectronic.com