The power system is the lifeblood of people all over the world, and the human, material and financial resources invested by each country are enormous. Electricity is also indispensable to the family and is indispensable for various industrial developments. There are many people who die from the power system. It is a pity that all we have to do is to improve the safety of the power system. The knowledge we say today may be what every electrician needs. It seems simple. Another important electrician knowledge - zero and grounding.
How to do groundingGenerally speaking, the depth of the grounding wire buried in the ground should not be less than 2m. When installing the grounding pole in a special place, if the depth is less than 2m, place 8kg of salt around the grounding electrode, about 30kg of wood carbon and add water to reduce the grounding resistance. If two or more grounding poles are used, what is the argon argon between the poles? .5m to reduce the ground resistance of the ground. In strongly corrosive soils, copper or galvanized grounding poles should be used. At the same time, the grounding pole should not be buried in the garbage layer and the ash layer area. The grounding pole laid in the ground should not be painted to avoid excessive grounding resistance.

Option 1: Ground pile
1. In the vicinity of the machine room, 4 or more 2.5m angle steels (45mm*45mm) are driven into the ground at a distance of 80cm from the ground, and each angle steel is 2m apart.
2. Four angle steels are welded together in series with flat steel (30mm*3mm).
3. Use galvanized flat steel (30mm*3mm) to weld any angle of angle steel as ground wire lead to the wall 2m.
4. The resistance tester measures the resistance of the ground net to be less than or equal to 4Ω. Otherwise, add the pile or use the field character to solve it.
5. Use 25mm square copper wire and ground wire lead to connect into the room through the copper wire nose.
6. Connect the signal lightning arrester ground wire and the electrostatic ground wire.
Option 2: buried copper plate
1. Dig a hole of 250cm*150cm*300cm near the machine room, sprinkle some sodium chloride on the bottom of the pit, and bury it in a copper plate (1500mm*600mm*3mm). The depth of the pit is subject to water, but at least greater than 200 cm.
2. The flat steel (30mm*3mm) and the copper plate are welded together with copper solder, and the ground is led out as a lead.
3. Weld the galvanized flat steel and flat steel leads together and lead them out 2m from the wall.
4. The tester measures the resistance of the ground net to be less than or equal to 4 ohms.
5. Use 25mm square copper wire and ground wire lead to connect into the room through the copper wire nose.
6. Connect the signal lightning arrester ground wire and the electrostatic ground wire.
Grounding principleIn the neutral point ungrounded system, when the equipment with protective grounding leaks, the leakage voltage forms a loop through the line to ground, which reduces the voltage of the leakage device shell. Since the grounding resistance of the human body is much larger than the protective grounding resistance, the current flowing through the human body is greatly increased. Reduced, reducing the risk of electric shock. In the direct grounding system of the neutral point, when the equipment of the protective earthing device leaks, it is essentially single-phase grounding. The leakage current forms a loop through the protective earthing body and the earth and the neutral ground of the transformer. Since the earthing resistance of the human body is much larger than the protective earthing resistance, the flow The current through the human body is greatly reduced, and the single-phase short-circuit current is accelerated by the protection action to cut off the current.
Grounding precautions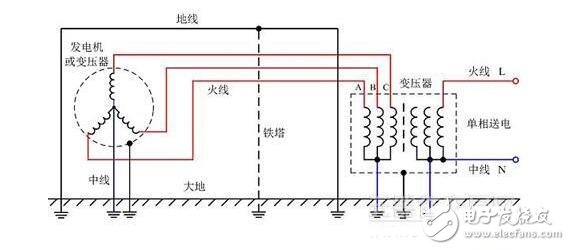
Pay attention to the following points when installing or removing the grounding wire:
1. When installing the grounding wire, first verify that there is no electricity on the line, and under the supervision of the guardian, operate by a skilled duty worker or electrician.
2. There must be two people to install the grounding wire. If it is a single person, only grounding the grounding of the grounding switch or using an insulated rod to ground the knife is allowed.
3. When installing the grounding wire, the grounding terminal must be connected first, followed by the conductor end, and the contact must be good and the winding is not allowed. When the ground wire is removed, the opposite is true. Insulation rods and insulated gloves should be used when installing or removing the grounding wire.
4. When installing the grounding wire for the multi-layer power line erected on the same pole, first hang the low voltage and then hang the high voltage; first hang the “ground†and then hang the “fireâ€; first hang the lower layer and then hang the upper layer. When the ground wire is removed, it is the opposite of this procedure. When installing or removing the grounding wire, use an insulating tie rod, and the human body is not allowed to touch the grounding wire.
5. When installing a ground wire on a device with a capacitor, discharge the device beforehand.
6. The cross-section of the grounding wire shall comply with the requirements of short-circuit current, and shall not be less than 25 mm2 of stranded bare copper flexible conductor, and shall be fixed on the conductor by a special clamp. It is forbidden to ground or short-circuit by winding. There should be no fuses or switches between the ground wire and the service section. Will there be any charge on the conductor ground?
How to connect zero and how it works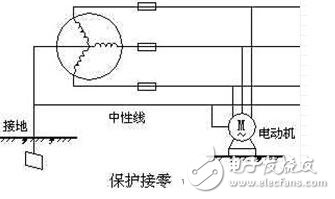
In a zero-connected power grid with a voltage lower than 1000 volts, if the electrical equipment is charged due to insulation damage or accidental conditions, a single-phase short-circuit of the phase-to-neutral line is formed, and the protection device on the line (automatic switch or The fuses act quickly and cut off the power supply, so that the metal part of the device does not have dangerous voltage for a long time, which ensures personal safety.
In a multi-phase AC power system, the neutral point of the star-connected winding is directly grounded to the same potential as the earth, that is, zero potential. A wire drawn from a neutral point of the ground is called a neutral line. On the same power supply electrical equipment, some equipment is not allowed to be protected to zero, and the other part is protected ground. Because when the protective earthing device is energized, if the grounding resistance r'D is large and the fault current ID is insufficient to operate the protection device, the voltage U0=IDrD always exists on the neutral line due to the existence of the working resistance rD. At this time, there is a dangerous voltage U0 on the outer casing of the protection zero device for a long time, which endangers personal safety.
Protection and zero connection is the way in which the metal part of the equipment is not charged under normal conditions, and the wire is directly connected to the system. Take the protection and zero connection method to ensure personal safety and prevent electric shock accidents.
The difference between grounding and zeroingZero connection means that the uncharged part of the metal casing of the electrical equipment is connected to the neutral line of the three-phase power supply and is called neutral zero. Grounding If the electrical equipment is protected and grounded, the current through the human body is only a part of the total grounding current. Since the grounding resistance is parallel with the human body resistance, the smaller the grounding resistance, the smaller the current flowing through the human body. The grounding resistance is within the proper range to ensure personal safety. Therefore, in this neutral point ungrounded (insulated) system, any metal part that may exhibit a ground voltage due to insulation damage (normally uncharged) should be grounded. This is the protective ground. The so-called protection and zero connection is to tightly connect the metal parts of the electrical equipment that are not charged under normal conditions with the zero line of the power grid, effectively protecting the safety of the person and equipment. In a three-phase four-wire system where the neutral point of the transformer is directly grounded, it is usually used as a safety measure. In this case, if one phase of the live part touches the device casing, the phase line is zeroed through the equipment casing. Single phase short circuit of the line. The short-circuit current is always many times higher than the normal operating current, enabling the protection device on the line to act quickly, thus removing the faulty part from the power supply and ensuring safety. In the 380/220V three-phase four-wire neutral point directly connected to the power grid, regardless of the environment, any metal part that may exhibit ground voltage due to insulation damage shall be connected to zero. It refers to the grounding of the metal parts of the electrical equipment without the point and the connection with the earth. It is called grounding, also called repeated zero.
Small class of knowledge: What should I do with a ground fault?The ground fault and its main characteristics are as follows: (1) When one phase (such as phase A) is not completely grounded, that is, through high resistance or arc grounding, the voltage of the fault phase is lowered, and the voltage of the non-fault phase is increased. High, they are greater than the phase voltage, but do not reach the line voltage. The voltage at the opening triangle of the voltage transformer reaches the setting value, and the voltage relay operates to send a ground signal.
(2) If phase A is completely grounded, the voltage of the fault phase drops to zero, and the voltage of the non-fault phase rises to the line voltage. At this time, 100V voltage appears at the opening triangle of the voltage transformer, and the voltage relay operates to send a ground signal.
(3) One phase (A phase) is broken or the fuse is blown on the high voltage side of the voltage transformer. At this time, the indication of the fault phase is not zero. This is because the phase voltmeter passes through the transformer coil and other in the secondary circuit. The two-phase voltmeter forms a series circuit with a relatively small voltage indication, but not the actual voltage of the phase, and the non-fault phase is still the phase voltage. A voltage value of about 35V will appear at the triangle of the transformer opening, and the relay will be activated to send a ground signal.
(4) Due to the presence of capacitive and inductive parameters in the system, especially ferromagnetic inductive components with iron cores, ferromagnetic resonance occurs when the parameter combinations are not matched, and the relay acts to give a ground signal.
(5) False grounding of the no-load busbar. When the busbar is running at no load, a three-phase voltage imbalance may occur and a ground signal is issued. But when you send a line, the grounding phenomenon will disappear by itself.
Arc ground fault
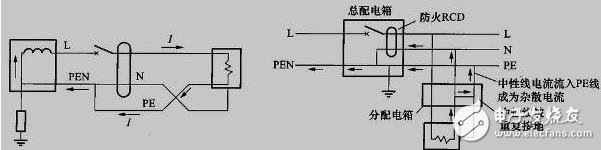
(1) The discharge capacitor current caused by the sudden decrease of the phase voltage. This current flows through the bus to the fault point, and the discharge current decays rapidly. The oscillation frequency is as high as several tens of kilohertz or even hundreds of kilohertz. The oscillation frequency is mainly determined by the grid line. The parameters, the location of the fault point, and the value of the transition resistance.
(2) The charging capacitor current caused by the sudden rise of the non-faulty phase voltage, which is formed by the transformer coil to form a loop. Since the inductance of the entire circulation loop is large, the charging current is attenuated slowly and the oscillation frequency is also low. Due to the high frequency of discharge current and fast decay. The effect of the ground selection line is not large; the charging current has a large amplitude, a low frequency, and a slow attenuation speed, which is beneficial for measurement and plays a major role in ground selection.
(3) The characteristics of transient components are basically not affected by the neutral grounding method. The zero-sequence current of each line is mainly the transient component of high-frequency attenuation, and the transient component can reach several times and several times of the steady-state component of power frequency. Ten times or even hundreds of times.
(4) The frequency of the transient component when the arc is grounded is related to various factors such as the grid structure, transformer parameters, and fault location. The value is an uncertain value. However, the zero-sequence transient current of the faulty line and the non-faulty line have the same characteristics such as frequency and attenuation speed. Regardless of the grounding mode, the magnitude of the zero-sequence transient current of the non-faulty line is proportional to the magnitude of the capacitance of the line to ground, and the zero-sequence transient current of the fault line is equal to the sum of the zero-sequence transient currents of all non-faulty lines, and The opposite direction. This is the same as the zero-sequence steady-state current characteristic in a neutral point ungrounded system.
(5) When the grounding resistance is small, the transient component is much larger than the steady-state component. However, the magnitude of the zero-sequence transient current decreases exponentially with the increase of arc resistance, and the decay rate of zero-sequence transient current increases rapidly with the increase of arc resistance.
Single phase ground fault
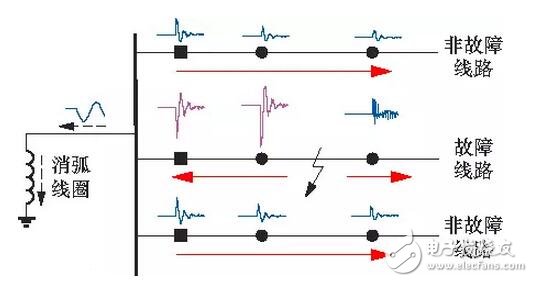
1 After a single-phase ground fault occurs, the duty officer should immediately return to the sound, make a record, promptly report the duty schedule and relevant responsible personnel, and find the ground fault according to the command of the duty dispatcher, but the specific search method is performed by the on-site duty officer himself. select.
2 Check the electrical equipment in the station for obvious signs of failure. If you can't find the fault point, look for the grounding of the line.
3 The busbars are operated in sections, and the parallel-running transformers are operated in series to determine the single-phase grounding area.
4 Pull on the busbar reactive compensation capacitor breaker and the no-load line. For multiple power lines, the load should be shifted and the power supply mode changed to find the ground fault point.
5 Use the pull-and-pull method to test and find the fault point. When the grounding phenomenon of a circuit breaker is broken, it can be judged as the fault line, and immediately report to the dispatcher of the duty, and at the same time, the fault line Circuit breakers, disconnectors, wall bushings and other equipment for further inspection.
(2) Requirements for handling ground faults:
1 When looking for and handling single-phase ground faults, safety measures should be taken to ensure personal safety. When the equipment is grounded, the indoors shall not be within 4m of the fault point, and the outdoor shall not be within 8m of the fault point. Workers entering the above range must wear insulated boots, wear insulated gloves, and use special tools.
2 In order to reduce the scope and negative impact of power outages, when searching for single-phase ground faults, first try to pull the lines with long lines, many branches, multiple faults and light loads, and secondary power, and then try to pull the lines short. A line with heavy load, few branches, and important point properties. Dual power users can switch the power supply and try to pull it first. The dedicated line should be notified first. If the person concerned reports that there is a sign of failure on a line, you can try to pull the line first.
3 If the high voltage fuse of the voltage transformer is blown, it should not be replaced by ordinary fuse. It is necessary to use a porcelain tube fuse with a rated current of 0.5A filled with quartz sand. This fuse has good arc extinguishing performance and large current interrupting capacity, and has the effect of limiting short-circuit current [4].
(3) Attention to risk
In order to reduce the adverse effects of single-phase ground faults on the grid operation, not only the duty personnel are required to be familiar with the relevant operational procedures, understand the operation status of the equipment, continuously summarize the experience in practice, improve the ability to handle problems, and actively improve the equipment. Operating conditions, timely eliminate equipment defects, keep equipment clean, and improve equipment insulation level. At the same time, it is necessary to strengthen the maintenance, maintenance and management of the distribution line, improve the technical level of the maintenance personnel of the distribution line, shorten the time for finding and handling the ground fault, and restore the power supply to the user as soon as possible.
The ultra-thin precision cutting of the Anti-Peep Screen Protector means that you can enjoy a perfect touch screen experience without allowing anything on the screen to be peeped. Whether you place your phone horizontally or vertically, Privacy Screen Protector can protect your personal Information and sensitive information are protected from harm by strangers. People around you cannot see the contents of your phone, so your details are safe.
The use of soft TPU material can really cover the entire screen.
With self-healing function, it can automatically repair bubbles and scratches within 24 hours.
The 0.14mm Ultra-Thin Protective Film can maintain the sensitivity of the touch screen to accurately respond to your touch.
The oleophobic and waterproof coating prevents fingerprints, oil stains and other substances from adhering to it and keeps the screen clean.
If you want to know more about Privacy Screen Protector products, please click Product Details to view the parameters, models, pictures, prices and other information about Privacy Screen Protector products.
Whether you are a group or an individual, we will try our best to provide you with accurate and comprehensive information about Privacy Screen Protector!
Anti-Spy Hydrogel Screen Protector, Privacy Protection Film, Protection Film, Privacy Film, Privacy Screen Protective Film, Soft Film
Shenzhen Jianjiantong Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.jjthydrogelmachine.com