Recently, Nokia announced that it has gone through the $190 million acquisition of wearable device maker Withings, which has once again pushed the long-sleeved wearable device into the spotlight.
The addition of Nokia seems to have intensified competition, but it is precisely because this capital injection into the wearable device industry has added some vitality, but also to the shake-stable and persistent enterprises to give a shot. According to a recent industry report released by CIC, the average annual growth of wearables market shipments will reach 35% in the next five years. There are still plenty of market upsides for smart watches and smart bracelets.
But the industry can't be too optimistic, because the reality is still cruel, the technical challenges of wearable devices have not been broken for a long time, and the poor endurance of the user experience has not improved the user experience.

Can that continue to optimize the design?
As we all know, the endurance is mainly determined by two factors, namely battery capacity and power consumption. The higher the battery capacity, the better, and the power consumption needs to be minimized. Unfortunately, before new battery technologies or materials emerge, there is very little room for battery capacity to increase, so the pressure is almost on how to reduce power consumption.
For developers, the correct posture for a low-power design is:
First, select low-power devices (including modules and master chips);
Then, optimize the software algorithm;
Finally, the power consumption test is also the key.
Unlike most consumer electronics, wearable devices have tighter control over the power consumption of a single component and system. Nearly all internal hardware structures are accurately measured before the product leaves the factory, such as chips, sensors, displays, Wireless modules, etc., so developers can design a set of low-power systems and test equipment are inextricably linked.
At present, the mainstream testing companies in the industry include Keysight, Tektronix, Keithley and Rhodes and Schwartz. These brands are representatives of the high-end market, while domestic domestic measuring instruments are mostly positioned at the low end. SME. But wearables are just a segment of the test and measurement industry, and there aren't many low-power test solutions that companies can use directly.
So how do wearables companies choose?
It is not difficult to understand that the two factors of performance and price are the universal reference standard. Tuman Technology CEO Wang Wei told Lei Feng that equipment such as Agilent (Keysight) and Tektronix are more expensive than domestic brands because of their high precision. It is understood that these devices generally cost between tens of thousands and one million, while domestic products are much cheaper.
However, if the performance is more complicated, the sampling rate of the device (because the device sleeps to the running state for a very short time, it needs to capture the instantaneously changing current waveform), precision, bandwidth and memory depth, etc. Dazzling, so purchasing a suitable equipment has long been a technical activity. The following are the mainstream test equipment manufacturers and related test equipments compiled by Lei Feng. They are for your reference only!
Keysight
When it comes to Keysight, you have to make Amway a legendary company.
As a benchmark in the testing industry, Agilent was the first manufacturer to test and measure instruments from Hewlett-Packard in March 1999. In November of the same year, it was listed as an independent company on the New York Stock Exchange. However, its test and measurement program dates back to 1939, and the founder is Bill. Bill Hewlett and David. David Packard is the legend of two Silicon Valley.
But everyone may not be so familiar with Keysight. In fact, Keysight is a subsidiary of Agilent that was split in 2013 and is fully responsible for the electronic measurement business. Agilent is the parent company and its business direction is in the field of biochemistry.
Before the split, Agilent was called "the king of global electronic measurement" by the industry, and the title after the split was also logically transferred to Keysight. As the company of Agilent's Electronic Measurement Division, it has been the world's number one position in the mid- to high-end oscilloscope market.
At present, the company has three high, medium and low product lines in the oscilloscope product line. Among them, the high-end and mid-end have introduced Keysight's unique indium phosphide semiconductor process, which is different from the brands used by Tektronix and other brands. Silicon technology, in terms of technology, we can divide test brands into two categories, one is Keysight and the other is called other companies. What is the difference between the two processes?
Taking the Infiniium V series oscilloscope as an example, because of the indium phosphide process, it has the characteristics of good impulse response, large operating voltage, good signal-to-noise ratio and high dynamic range. Therefore, other products can be spiked in measurement accuracy. In addition, the parameters of this series of equipment are leading level, the maximum storage depth is 2Gpts, the sampling rate is 80GSa/s, the bandwidth ranges from 8GHz to 33GHz, and the corresponding price is between 110,000 US dollars and 360,000 US dollars.
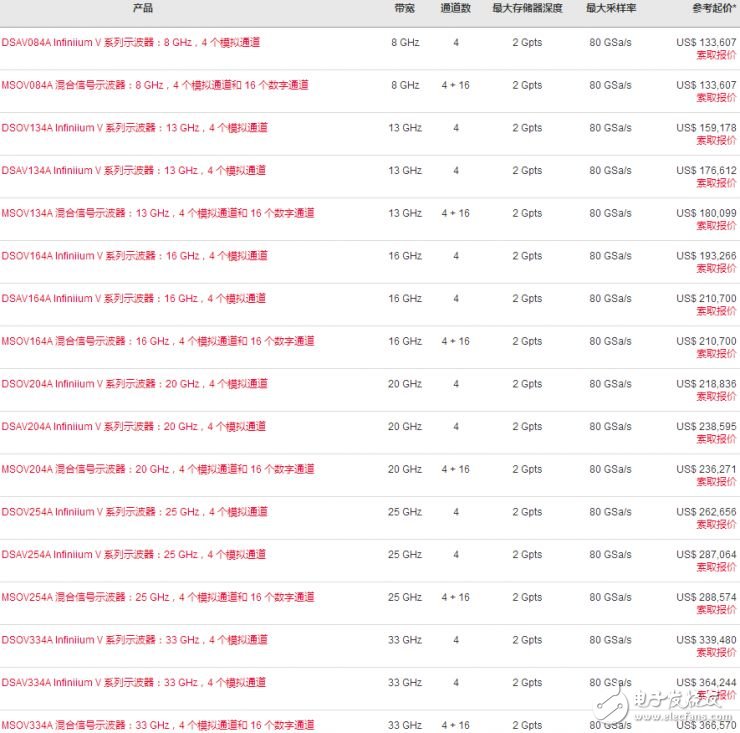
Of course, on low-end test equipment, Keysight has not adopted a more advanced indium phosphide process, such as the InfiniiVision 2000 X series.
In terms of power consumption testing, Keysight's N6705B DC power analyzer integrates the power supply with a digital multimeter, oscilloscope, arbitrary waveform generator and Data logger. The test current accuracy is up to the nanoamp level, and the oscilloscope bandwidth is 200 KHz. At 512 Kpts, the performance is average, but the main requirement is the accuracy and speed requirements of the wearable device test, which is priced at $8,240. The specific specifications are as follows:
The 4-slot mainframe can be installed with up to 4 modules for a total power of up to 600 W. More than 20 DC power modules are available (requires separate modules)
Voltmeter accuracy: 0.025% + 50 μV, up to 18 bits
Ammeter accuracy: 0.025% + 8 nA, up to 18 digits
Arbitrary waveform generator function: bandwidth up to 100 kHz, output power up to 300 W
Oscilloscope function: digitizes voltage and current, 200 kHz, 512 kpts, up to 18 bits
Data Logger function: measurement interval from 20 μs to 60 s, each data logger stores up to 500 million readings
4 GB non-volatile data memory for storing data records, oscilloscope traces, instrument settings
To sum up, Keysight's products are relatively complex, and the performance is also a ride, but the price of equipment is generally high.
Mini Jumper:The short-circuit cap is a 1.27mm,2.00mm, 2.54mm 5.08mm circuit sheet metal. As long as it is 2 pins, the short-circuit cap can be used to short it.
What is the function of the short circuit cap? Short circuit cap, I call it short circuit block. For example, if you use a single row of pins, you can use the short circuit block to short circuit the two adjacent pins (that is, to realize the connection on the circuit). For example, if you have a three wire pin, you can use a short circuit block to realize the function of dial switch.
Male Pin Headers & Min Jumper Series
Mini Jumper
ShenZhen Antenk Electronics Co,Ltd , https://www.antenk.com