Definition of the light distribution curve:
The light distribution curve is actually the distribution of light emitted by a luminaire or light source in space. It can record the luminous flux of the luminaire, the number of light sources, power, power factor, luminaire size, luminaire efficiency, including the manufacturer and model of the luminaire. Of course, the most important thing is to record the light intensity of the luminaire in all directions.
Classification of light distribution curves:
According to their symmetrical properties, the light distribution curve can be generally divided into: axially symmetric, symmetric and asymmetric light distribution.
Axial symmetry: Also known as rotational symmetry, it means that the light distribution curves in all directions are basically symmetrical. Generally, downlights and high bay lights are such light distributions.
Symmetry: When the C0° and C180° profiles of the luminaire are symmetrical, and the C90° and C270° profiles are symmetrical, such a light distribution curve is called symmetrical light distribution asymmetry: it means C0°-
180 ° and C90 ° - 270 ° any one of the sections with asymmetrical light distribution.
The light distribution curve can be generally divided into: according to its beam angle:
Narrow light distribution (< 20°)
Medium light distribution (20°> 40°)
Wide light distribution (> 40°)
In fact, there is no strict definition of each manufacturer's definition of width, medium and narrow is slightly different.
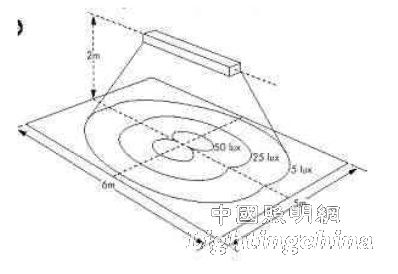
Said a half-day definition and classification. Let's take a look at the real thing - the light distribution curve of the bracket:
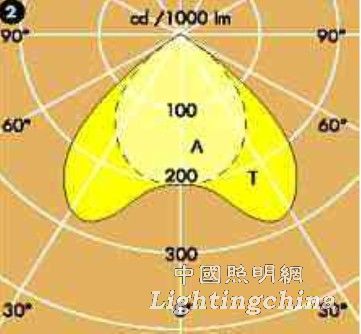
T = C0°-180°
A = C90°-270°